Section 4 - Evaluate Governance Risk Compliance (GRC) technical strategies and security operations strategies - Design a regulatory compliance strategy
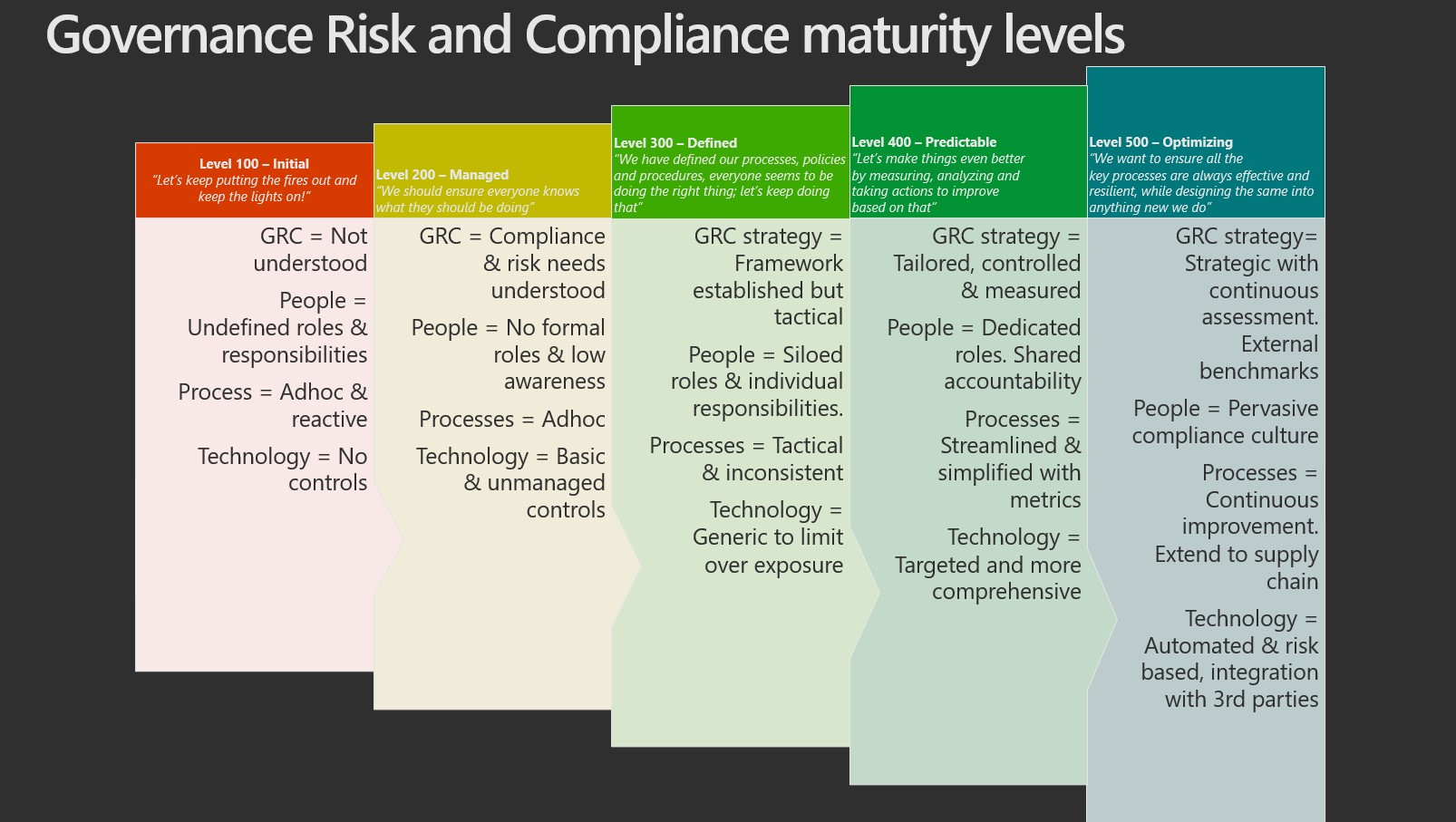
This is the fourth section to my SC-100 study guide and it will cover the following topics:
- Interpret compliance requirements and translate into specific technical capabilities (new or existing)
- Evaluate infrastructure compliance by using Microsoft Defender for Cloud
- Interpret compliance scores and recommend actions to resolve issues or improve security
- Design implementation of Azure Policy
- Design for data residency requirements
- Translate privacy requirements into requirements for security solutions
Interpret compliance requirements and translate into specific technical capabilities (new or existing)
Governance – How is the organization’s security going to be monitored, audited, and reported? Design and implementation of security controls within an organization is only the beginning of the story. How does the organization know that things are actually working? Are they improving? Are there new requirements? Is there mandatory reporting? Similar to compliance there may be external industry, government or regulatory standards that need to be considered.
Risk – What types of risks does the organization face while trying to protect identifiable information, Intellectual Property (IP), financial information? Who may be interested or could leverage this information if stolen, including external and internal threats as well as unintentional or malicious? A commonly forgotten but extremely important consideration within risk is addressing Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity.
Compliance – Are there specific industry, government, or regulatory requirements that dictate or provide recommendation on criteria that your organization’s security controls must meet?
Make a baseline
Microsoft has a tool that identifies gaps in your organization across key domains, as defined in Governance methodology of the Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework-organizational readiness, resource consistency, cost management, deployment acceleration, security baseline, and identity baseline.

Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework Governance Benchmark Tool
Adopt CAF model and study the available documentation
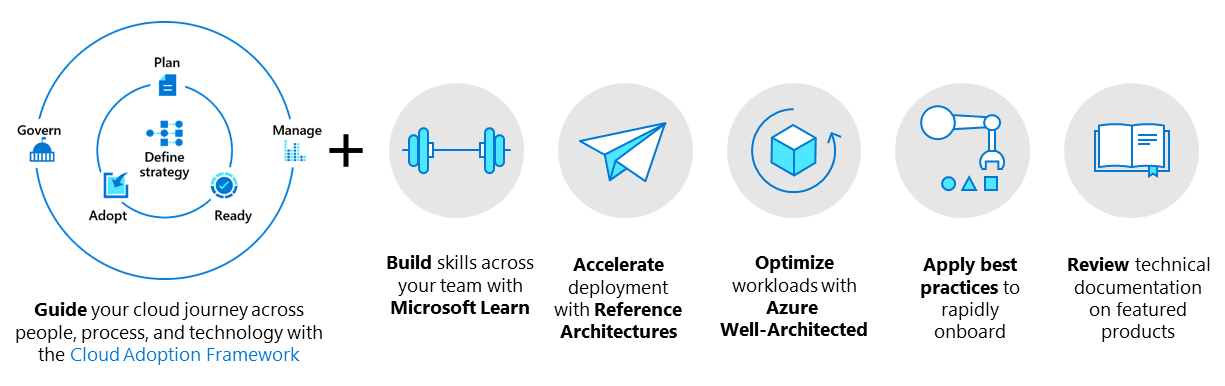
CAF
The Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure guides you through each consideration and implementation along the phases of your cloud adoption journey. Use the Cloud Adoption Framework across your organization to prepare decision makers, central IT, and the cloud center of excellence (CCoE) for your organization's cloud adoption efforts.

Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure - Cloud Adoption Framework

Well-Architected Framework
The Azure Well-Architected Framework provides a set of Azure architecture best practices (cost management, operational excellence, performance efficiency, reliability, and security) to help you build and deliver great solutions. The Well-Architected Framework outlines necessary considerations for the workload owner before initiating workload deployments.
| Pillar | Description |
|---|---|
| Reliability | The ability of a system to recover from failures and continue to function. |
| Security | Protecting applications and data from threats. |
| Cost Optimization | Managing costs to maximize the value delivered. |
| Operational Excellence | Operations processes that keep a system running in production. |
| Performance Efficiency | The ability of a system to adapt to changes in load. |

Azure Architecture Center
Reference architectures are templates of required components, and the technical requirements to implement them. Each reference architecture includes recommended practices, with considerations for scalability, availability, security, resilience, and other design aspects, including a deployable solution, or reference implementation. Reference architectures aid in accelerating deployment for a number of common scenarios.
Microsoft have released an consolidated center for different architectures, it’s an easy way to start the planning.

Azure Architecture Center - Azure Architecture Center
If you choose “Browse Azure architecture” from the main page.
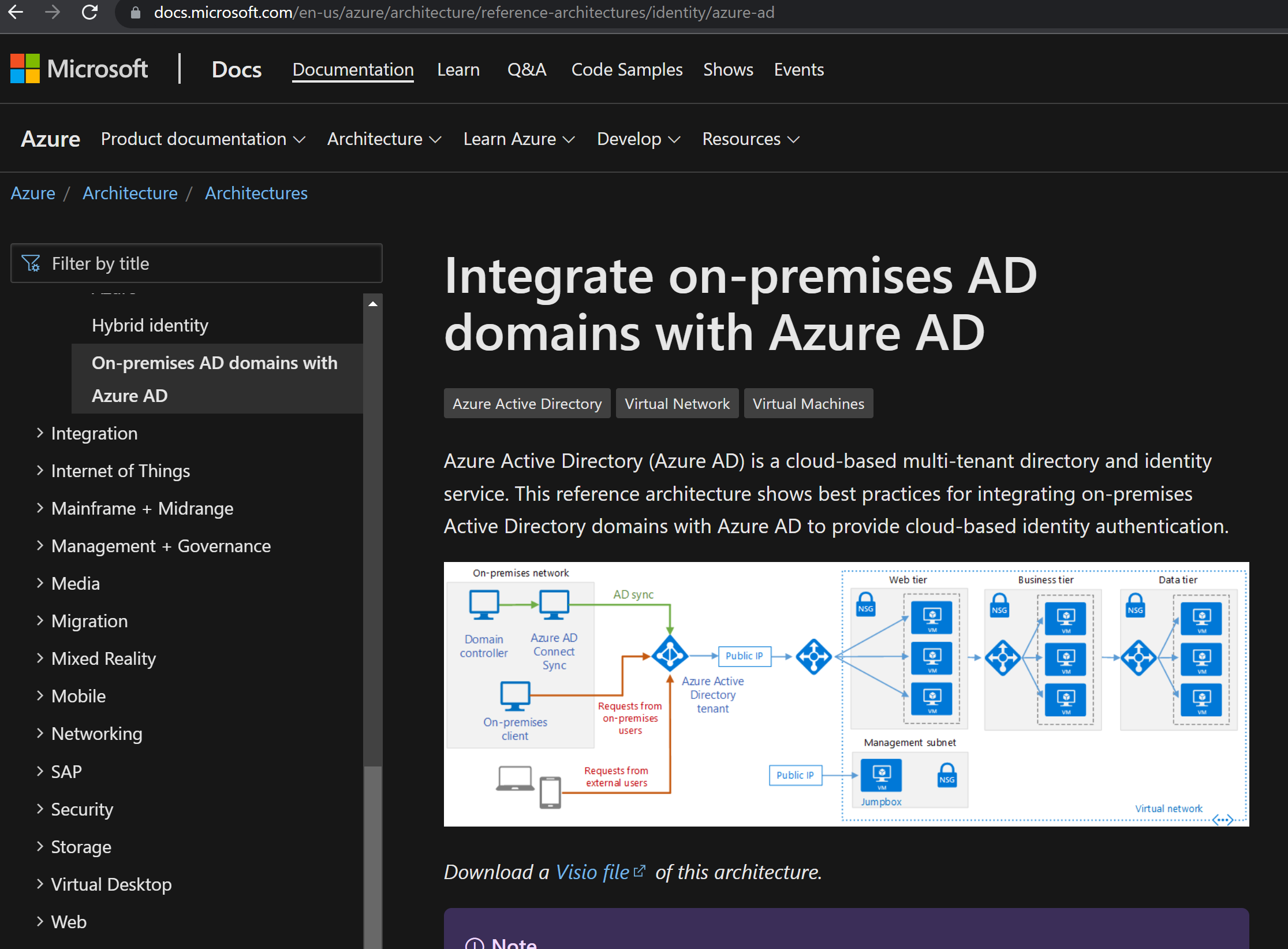
There you will find example guidance for integrating your On-premises AD securely to Azure AD.

Security best practices
Best practices help you build reliable, scalable, and secure applications in the cloud. They offer you guidelines and tips for designing and implementing efficient and robust systems, mechanisms, and approaches to onboard assets using Azure Arc, ARM templates, and various Azure products.

Security best practices and patterns - Microsoft Azure

Workload prioritizing
Featured Azure products provide information about the products that support your Azure strategy. Use proven combinations of Azure products and services to solve your business problems. Get started with documentation and reference architectures, follow best practices guidance for scenarios, and implement solutions for common workloads on Azure.

Define and prioritize workloads for cloud adoption - Cloud Adoption Framework

Microsoft Learn
Microsoft Learn is an online free training platform. Guided, interactive, hands-on Learn modules help you to gain required skills so you can implement, maintain, and support solutions in the cloud, including role-based training and learning paths for Azure developers, solution architects, and administrators.

Browse all - Learn
Technical tools to meet governance and compliance
| Capability | Description | More information |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft 365 Defender portal | Microsoft 365 Defender portal provides security administrators and other risk management professionals with a centralized hub and specialized workspace that enables them to manage and take full advantage of Microsoft 365 intelligent security solutions for identity and access management, threat protection, information protection, and security management. | Microsoft 365 Defender portal |
| Microsoft Purview compliance portal | Microsoft Purview compliance portal provides easy access to the data and tools you need to manage your organization's compliance needs. | Microsoft Purview compliance portal |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a unified infrastructure security management system that strengthens the security posture of your data centers, and provides advanced threat protection across your hybrid workloads in the cloud - whether they're in Azure or not - as well as on premises. | Microsoft Defender for Cloud documentation |
| Management Groups | If your organization has many subscriptions, you may need a way to efficiently manage access, policies, and compliance for those subscriptions. Azure management groups provide a level of scope above subscriptions. You organize subscriptions into containers called "management groups" and apply your governance conditions to the management groups. | Organize your resources with Azure management groups |
| Azure Policy | Azure Policy is a service in Azure that you use to create, assign, and manage policies. These policies enforce different rules and effects over your resources, so those resources stay compliant with your corporate standards and service level agreements. | Azure Policy documentation |
| Azure Blueprints | Azure Blueprints enables cloud architects and central information technology groups to define a repeatable set of Azure resources that implements and adheres to an organization's standards, patterns, and requirements. Azure Blueprints makes it possible for development teams to rapidly build and stand up new environments with trust they're building within organizational compliance with a set of built-in components -- such as networking -- to speed up development and delivery. | Azure Blueprints documentation |
Evaluate infrastructure compliance by using Microsoft Defender for Cloud
What regulatory compliance standards are available?
By default, every Azure subscription has the Azure Security Benchmark assigned. This is the Microsoft-authored, Azure-specific guidelines for security and compliance best practices based on common compliance frameworks.
Available regulatory standards:
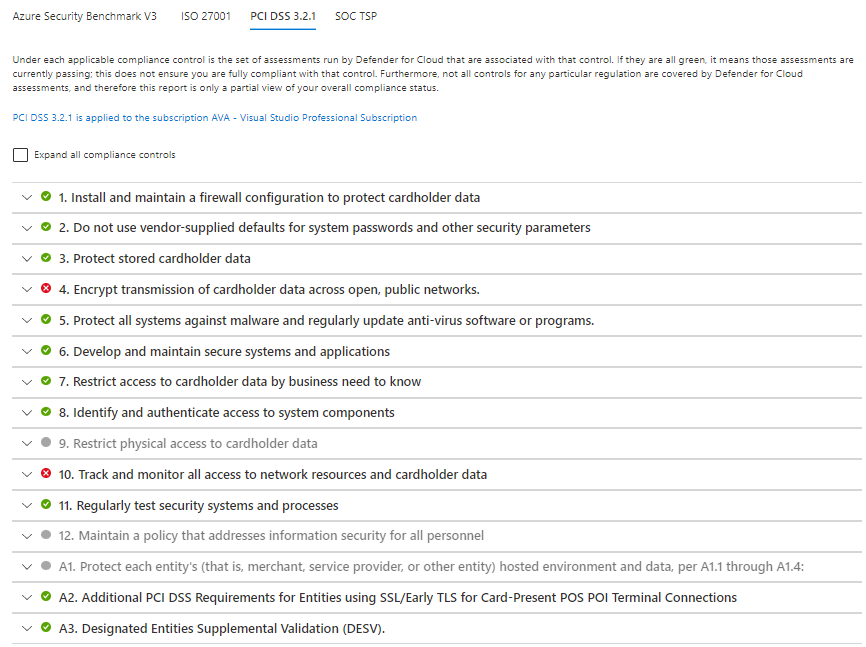
- PCI-DSS v3.2.1:2018
- SOC TSP
- NIST SP 800-53 R4
- NIST SP 800 171 R2
- UK OFFICIAL and UK NHS
- Canada Federal PBMM
- Azure CIS 1.1.0
- HIPAA/HITRUST
- SWIFT CSP CSCF v2020
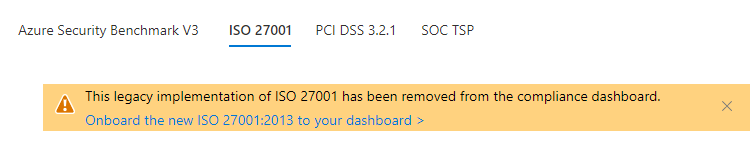
- ISO 27001:2013
- New Zealand ISM Restricted
- CMMC Level 3
- Azure CIS 1.3.0
- NIST SP 800-53 R5
- FedRAMP H
- FedRAMP M
ASC
Azure Security Center is located under Defender for Cloud https://portal.azure.com/#view/Microsoft_Azure_Security/ComplianceBlade
From here you can see the regulatory compliance status for your services
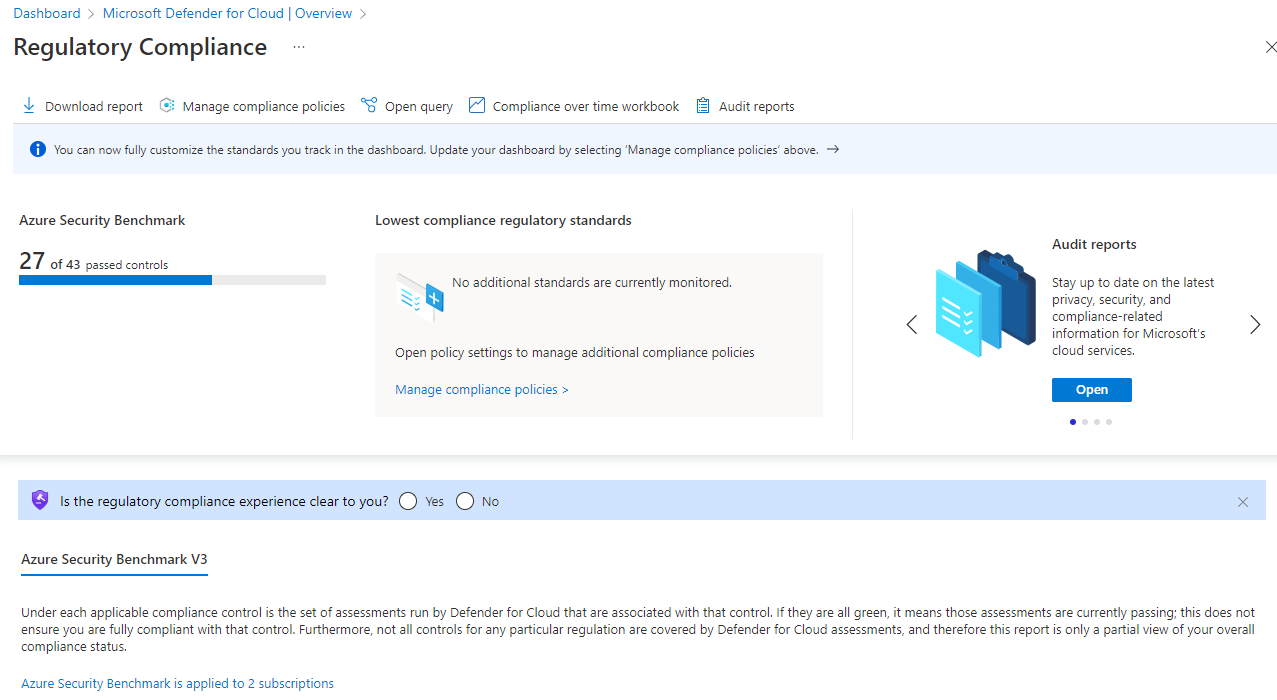
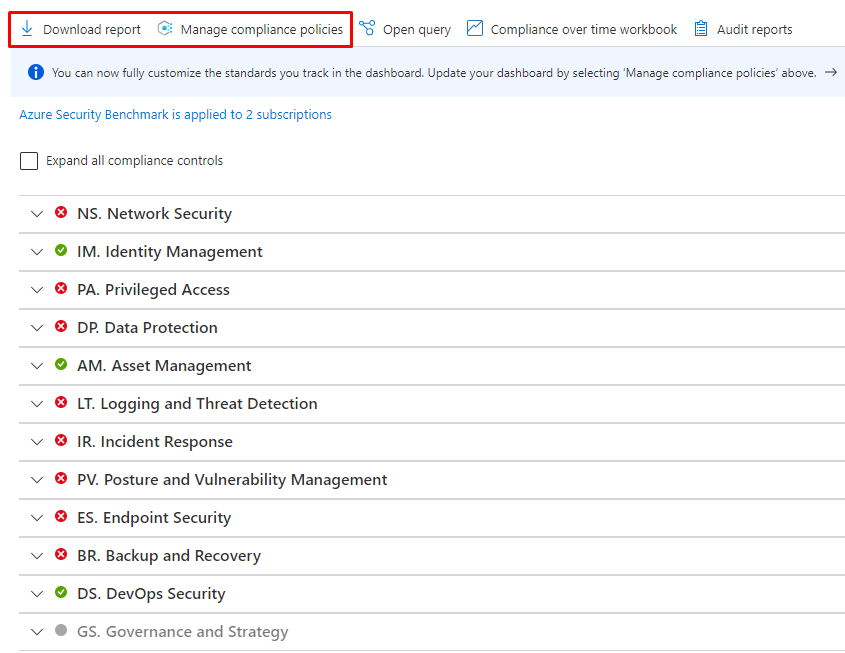
And you can download the report and edit Azure Policies to comply with the regulations.
ISO 27001:2013
PCI DSS 3.2.1
SOC TSP
Trust Services Criteria (TSC) replaced "Trust Services Principles (TSP)" for SOC reporting.
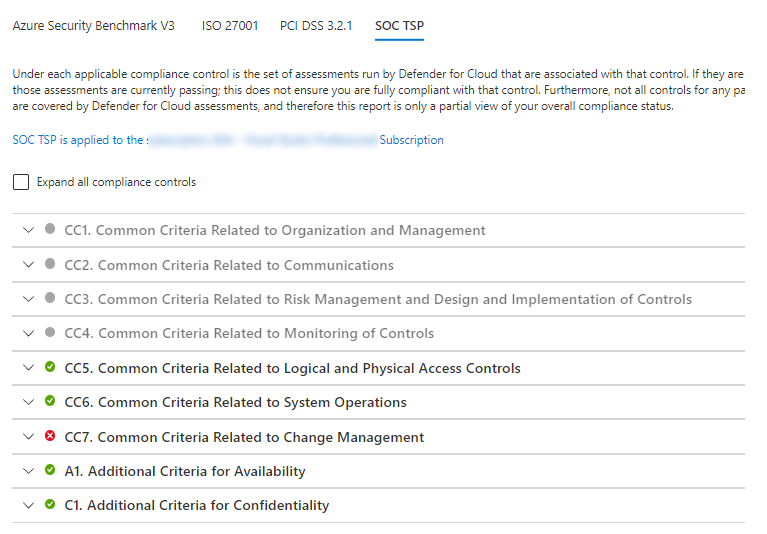
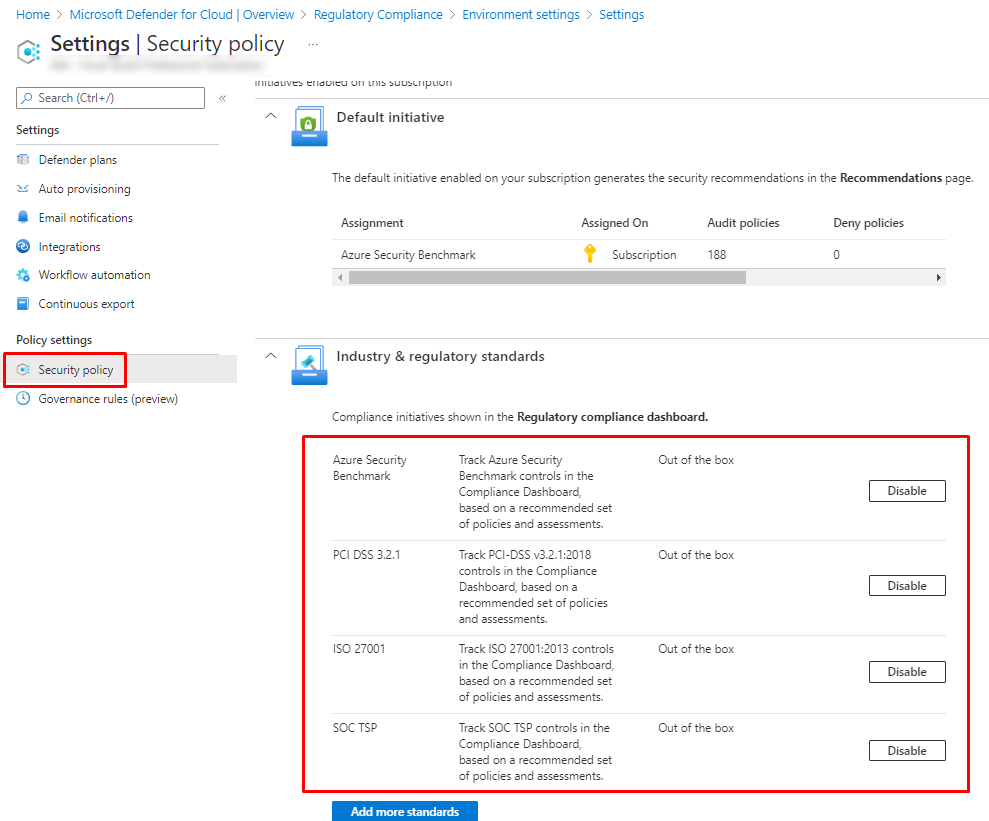
Removing or adding an applied policy
Under Security policy you can disable the default out of the box policies and add more.
Permissions needed
| Security Reader | View permissions for Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Can view recommendations, alerts, a security policy, and security states, but cannot make changes. | 39bc4728-0917-49c7-9d2c-d95423bc2eb4 |
| Resource Policy Contributor | Users with rights to create/modify resource policy, create support ticket and read resources/hierarchy. | 36243c78-bf99-498c-9df9-86d9f8d28608 |
Interpret compliance scores and recommend actions to resolve issues or improve security
Purview Compliance manager
Compliance is based on organization industry or customer requirements.
Compliance improves your security posture. It will help you define baseline for security requirements, but also minimize costs during possible breaches and lost of classified internal data.
Microsoft made and Compliance Manager portal that has standards based on industry and regulations.
The following compliance templates are available in the following subscriptions.
| License Type | Assessment Templates (included by default) |
| Microsoft 365 or Office 365 A1/E1/F1/G1 | Data Protection Baseline |
| Microsoft 365 or Office 365 A3/E3/F3/G3 | |
| Microsoft 365 or Office 365 A5/E5/G5 | Data Protection Baseline |
| Microsoft 365 A5/E5/F5/G5 Compliance | EU GDPR |
| Microsoft 365 A5/E5/F5/G5 eDiscovery and Audit | NIST 800-53 |
| Microsoft 365 A5/E5/F5/G5 Insider Risk Management | ISO 27001 |
| Microsoft 365 A5/E5/F5/G5 Information Protection and Governance | Customer Assessments |
| CMMC Level 1-5 (only available for G5) |
And there is also premium templates available for purchase.

Microsoft Purview Compliance Manager templates list - Microsoft Purview (compliance)
And premium templates are available in all subscriptions. There was a change at 7/2021 from Microsoft.
“To meet customers where they are in their compliance journey, we are excited to announce that Compliance Manager premium assessment templates will no longer require a Microsoft 365 E5 or Office 365 E5 license as a prerequisite. This update enables all enterprise customers to assess compliance with the regulations most relevant to them and meet their unique compliance needs. Starting July 1st, 2021, all Enterprise customers, both commercial and government, can purchase premium assessment templates as long as they have any Microsoft 365 or Office 365 subscription.”

Use Premium Assessments in Microsoft Compliance Manager to Meet Your Regulatory Compliance Needs
So, there is many points why to use Compliance Manager.
- Pre-built assessments for common industry and regional standards and regulations, or custom assessments to meet your unique compliance needs.
- Workflow capabilities to help you efficiently complete your risk assessments through a single tool.
- Detailed step-by-step guidance on suggested improvement actions to help you comply with the standards and regulations that are most relevant for your organization. For actions that are managed by Microsoft, you’ll see implementation details and audit results.
- A risk-based compliance score to help you understand your compliance posture by measuring your progress in completing improvement actions.
Compliance Manager Secure Score.
Your initial score is calculated according to the default Data Protection Baseline assessment provided to all organizations. Upon your first visit, Compliance Manager is already collecting signals from your Microsoft 365 solutions. You’ll see at a glance how your organization is performing relative to key data protection standards and regulations, and see suggested improvement actions to take.
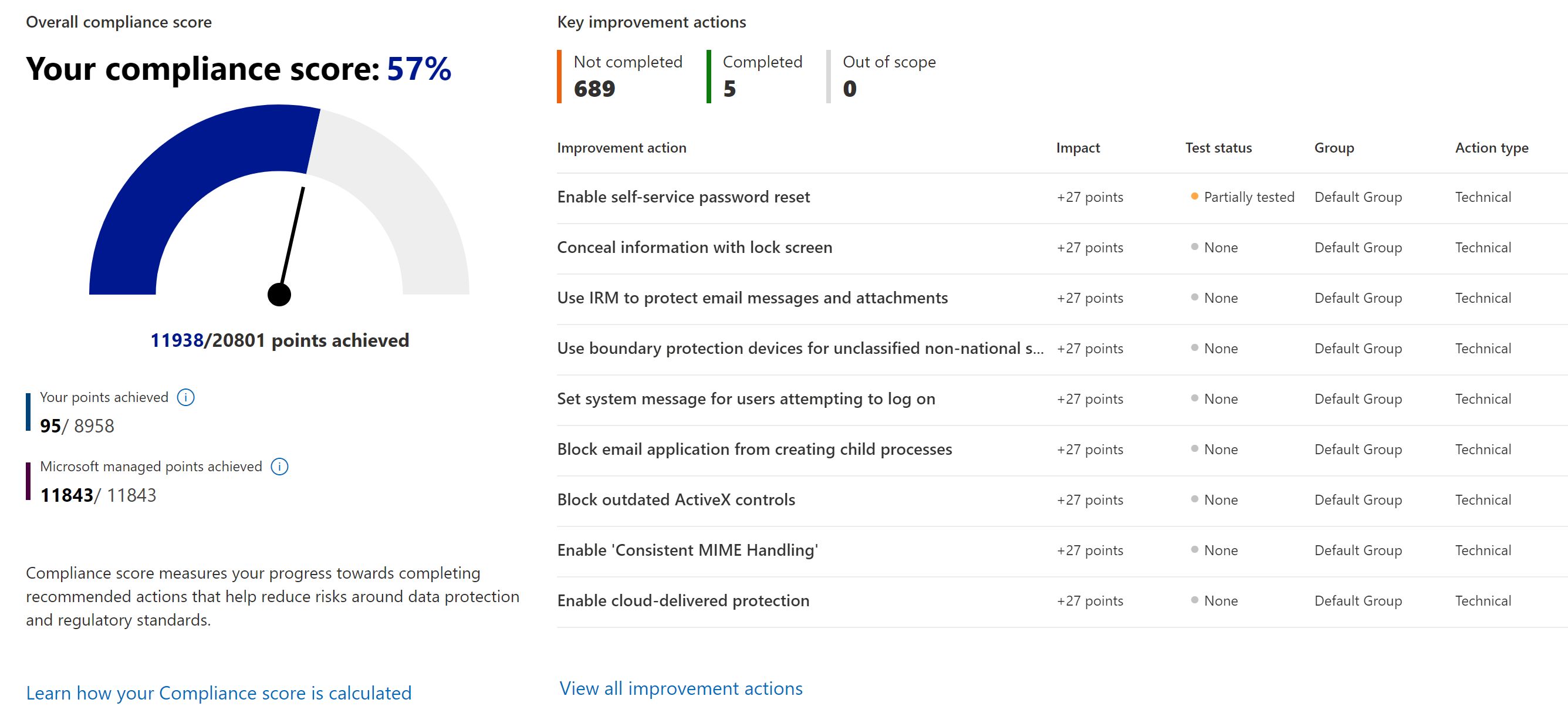
You can also add your own assessment from the templates. Be default the following assessment is enabled in every tenant.
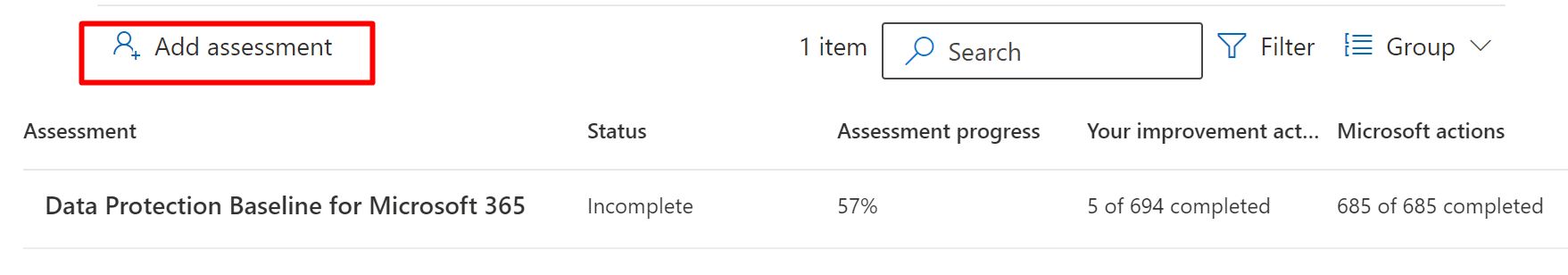
And when you click add you create from a template.
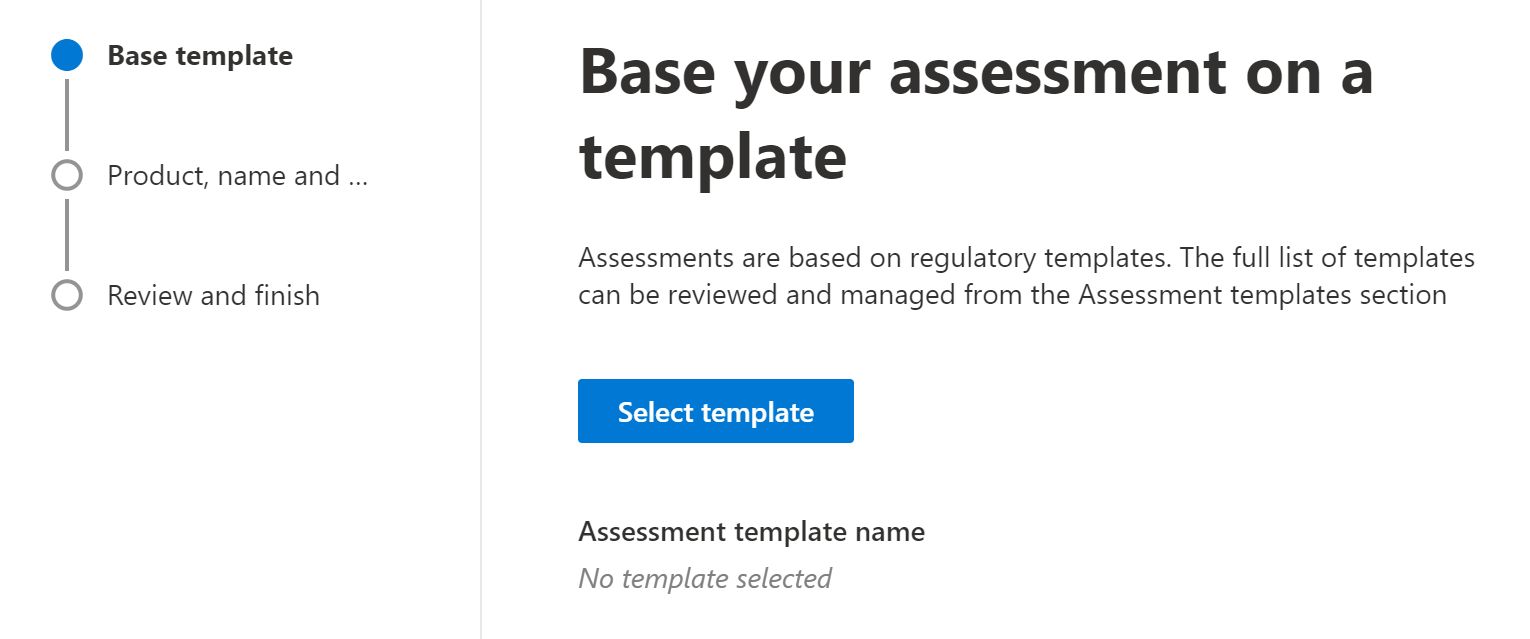
I will choose CIS Microsoft 365 Foundations Benchmark which has two levels.
- Level 1—Recommended minimum security settings that should be configured on any system and should cause little or no interruption of service or reduced functionality.
- Level 2—Recommended security settings for highly secure environments and could result in some reduced functionality.
And controls they have.
| Section | Description | Amount of controls |
| Account/Authentication policies | Recommendations related to setting the appropriate account and authentication policies. | 8 |
| Application permissions | Recommendations related to the configuration of application permissions within Microsoft 365. | 4 |
| Data management | Recommendations for setting data management policies. | 6 |
| Email security/Exchange Online | Recommendations related to the configuration of Exchange Online and email security. | 13 |
| Auditing policies | Recommendations for setting auditing policies on your Microsoft 365 tenant. | 14 |
| Storage policies | Recommendations for securely configuring storage policies. | 2 |
| Mobile device management | Recommendations for managing devices connecting to Microsoft 365. | 13 |
| Total recommendations | 60 |
And when you start applying the template, you can copy the information from old assessments or create a new one.
And when you are done with applying process, you will start to see assessment running in our tenant.
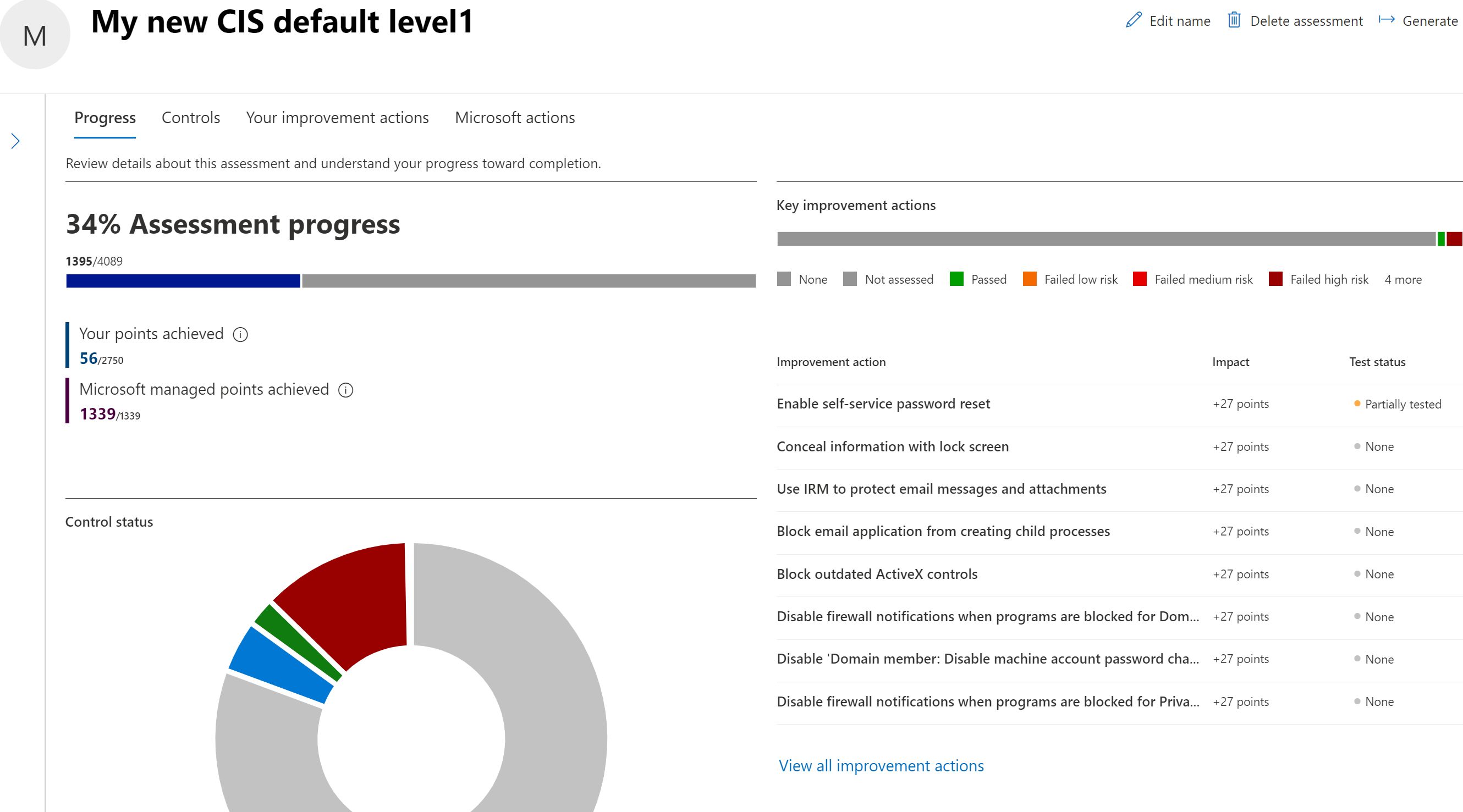
So, lets open one and you will see what is inside.
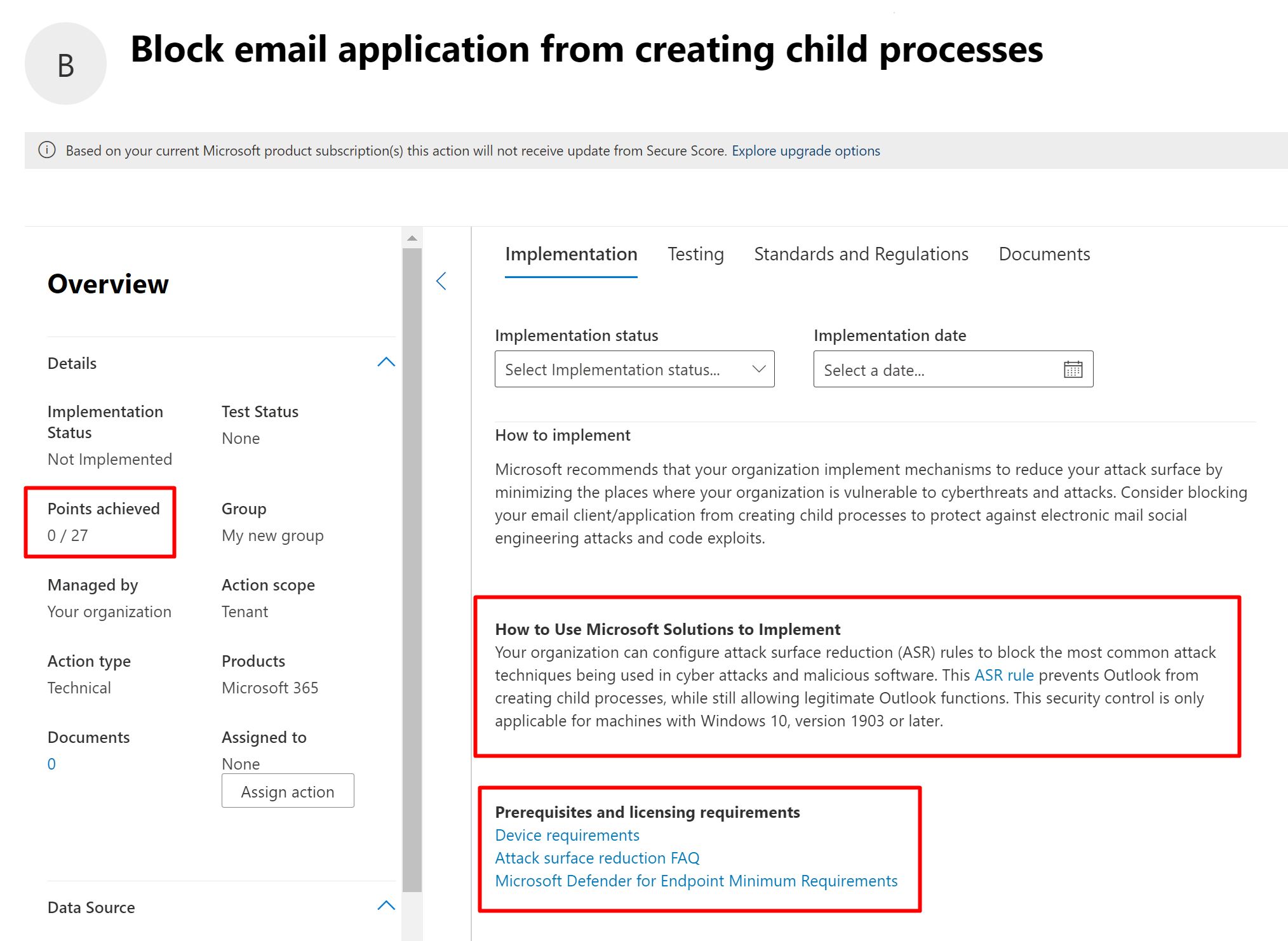
On the left you will points that this will affect on the Compliance and Secure Score. And on the rights instructions how to implement and what licenses it requires, so it’s a one-step shop for all info.
You can select implementation status or let it be discovered when you run the assessment again.
You can see the policies on the same page and like you would imagine CIS policy has a lot more actions inside.
Score calculation
In Compliance Manager you can find points under each action. In example 27 is points from a mandatory action.
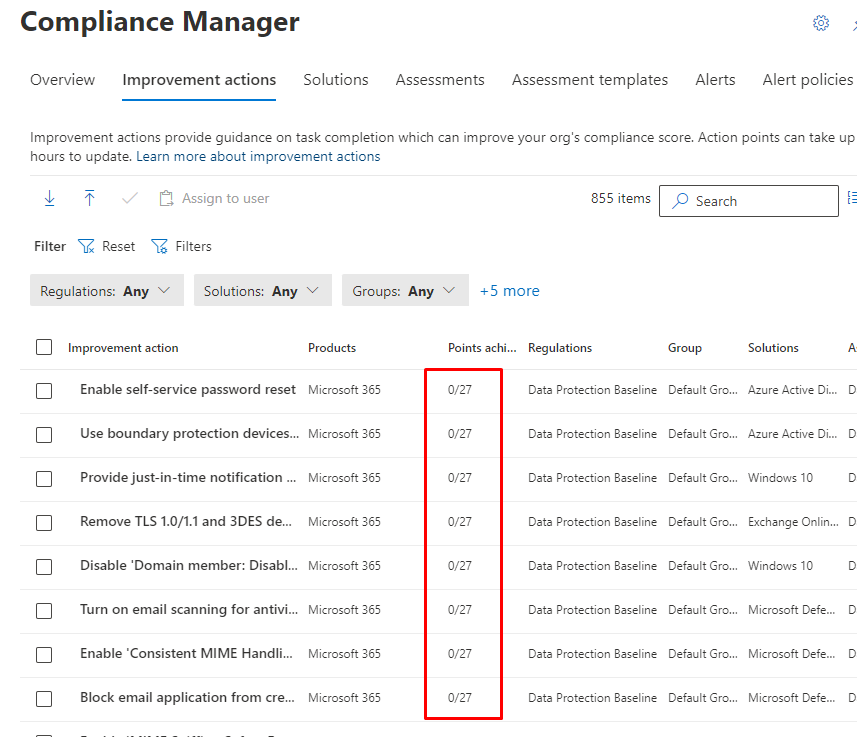
And 9 points for preventive actions
Actions are assigned a score value based on whether they’re mandatory or discretionary, and whether they’re preventative, detective, or corrective.
Mandatory and discretionary actions
- Mandatory actions can't be bypassed, either intentionally or accidentally. An example of a mandatory action is a centrally managed password policy that sets requirements for password length, complexity, and expiration. Users must follow these requirements to access the system.
- Discretionary actions rely upon users to understand and adhere to a policy. For example, a policy requiring users to lock their computer when they leave it is a discretionary action because it relies on the user.
Preventative, detective, and corrective actions
- Preventative actions address specific risks. For example, protecting information at rest using encryption is a preventative action against attacks and breaches. Separation of duties is a preventative action to manage conflict of interest and guard against fraud.
- Detective actions actively monitor systems to identify irregular conditions or behaviors that represent risk, or that can be used to detect intrusions or breaches. Examples include system access auditing and privileged administrative actions. Regulatory compliance audits are a type of detective action used to find process issues.
- Corrective actions try to keep the adverse effects of a security incident to a minimum, take corrective action to reduce the immediate effect, and reverse the damage if possible. Privacy incident response is a corrective action to limit damage and restore systems to an operational state after a breach.
Each action has an assigned value in Compliance Manager based on the risk it represents:
| Type | Assigned score |
|---|---|
| Preventative mandatory | 27 |
| Preventative discretionary | 9 |
| Detective mandatory | 3 |
| Detective discretionary | 1 |
| Corrective mandatory | 3 |
| Corrective discretionary | 1 |

Secure score in Defender for Cloud
You can also find Secure score from Defender, you can see history for Secure score and export and Governance report.
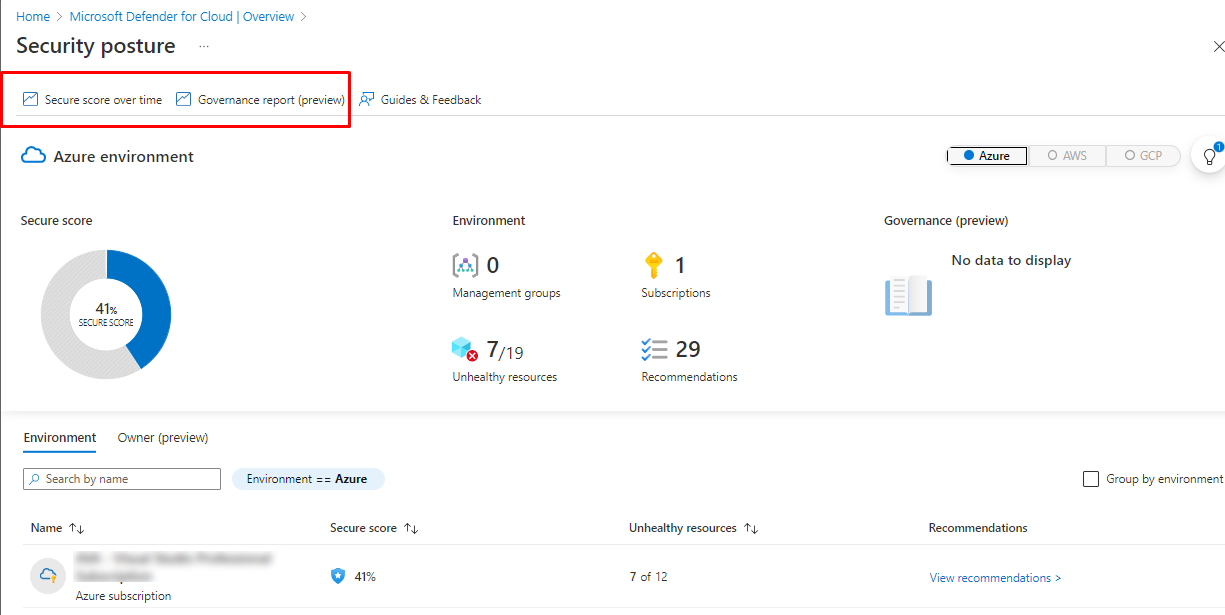
Continuous export
If you want to see the historical data, you have enable Continuous export function.

Continuous export can send Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s alerts and recommendations to Log Analytics or Azure Event Hubs
How the score is calculated?
You can see a Potential score estimation under the policy.
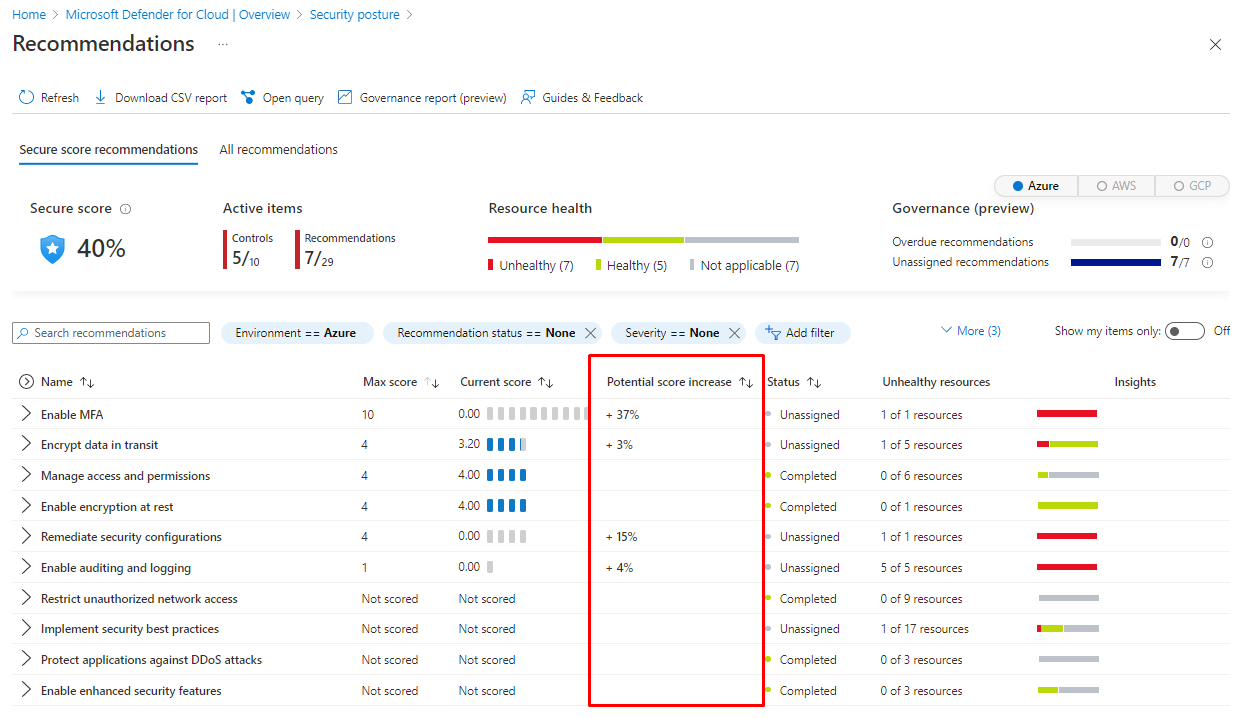
And here more info on the different factors

Security posture for Microsoft Defender for Cloud
In example for MFA
| Secure score | Security control and description | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | Enable MFA - Defender for Cloud places a high value on multi-factor authentication (MFA). Use these recommendations to secure the users of your subscriptions. There are three ways to enable MFA and be compliant with the recommendations: security defaults, per-user assignment, conditional access policy. Learn more about these options in Manage MFA enforcement on your subscriptions. | - MFA should be enabled on accounts with owner permissions on subscriptions - MFA should be enabled on accounts with write permissions on subscriptions |
Improve the score
To improve your secure score, remediate security recommendations from your recommendations list. You can remediate each recommendation manually for each resource, or use the Fix option (when available) to resolve an issue on multiple resources quickly. For more information, see Remediate recommendations.
You can also configure the Enforce and Deny options on the relevant recommendations to improve your score and make sure your users don't create resources that negatively impact your score.
More on policies on Azure Policy design.
Design implementation of Azure Policy
Azure Policy evaluates resources in Azure by comparing the properties of those resources to business rules. These business rules, described in JSON format, are known as policy definitions. To simplify management, several business rules can be grouped together to form a policy initiative (sometimes called a policySet). Once your business rules have been formed, the policy definition or initiative is assigned to any scope of resources that Azure supports, such as management groups, subscriptions, resource groups, or individual resources. The assignment applies to all resources within the Resource Manager scope of that assignment. Subscopes can be excluded, if necessary.
Azure Policy uses a JSON format to form the logic the evaluation uses to determine whether a resource is compliant or not. Definitions include metadata and the policy rule. The defined rule can use functions, parameters, logical operators, conditions, and property aliases to match exactly the scenario you want. The policy rule determines which resources in the scope of the assignment get evaluated.
Azure Policy Samples
GitHub - Azure/azure-policy: Repository for Azure Resource Policy built-in definitions and samples
Definition
You use JSON to create a policy definition. The policy definition contains elements for:
- display name
- description
- mode
- metadata
- parameters
- policy rule
- logical evaluation
- effect
Effect types
| Resource State | Effect | Policy Evaluation | Compliance State |
|---|---|---|---|
| New or Updated | Audit, Modify, AuditIfNotExist | True | Non-Compliant |
| New or Updated | Audit, Modify, AuditIfNotExist | False | Compliant |
| Exists | Deny, Audit, Append, Modify, DeployIfNotExist, AuditIfNotExist | True | Non-Compliant |
| Exists | Deny, Audit, Append, Modify, DeployIfNotExist, AuditIfNotExist | False | Compliant |
Initiative
You use JSON to create a policy initiative definition. The policy initiative definition contains elements for:
- display name
- description
- metadata
- parameters
- policy definitions
- policy groups (this property is part of the Regulatory Compliance (Preview) feature)
You need System Managed Identity for any remediation tasks.
Policy assignment to identify non-compliant resources
Identify non-compliant resources
| Resource State | Effect | Policy Evaluation | Compliance State |
|---|---|---|---|
| New or Updated | Audit, Modify, AuditIfNotExist | True | Non-Compliant |
| New or Updated | Audit, Modify, AuditIfNotExist | False | Compliant |
| Exists | Deny, Audit, Append, Modify, DeployIfNotExist, AuditIfNotExist | True | Non-Compliant |
| Exists | Deny, Audit, Append, Modify, DeployIfNotExist, AuditIfNotExist | False | Compliant |

Once you have create a definition, you can assign it. From the policy itself
Or from Assignments menu
Earlier we created only Deny and Disable effects but we can also add Audit to the effects and make it as default.
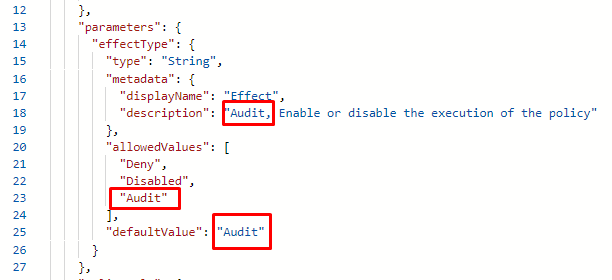
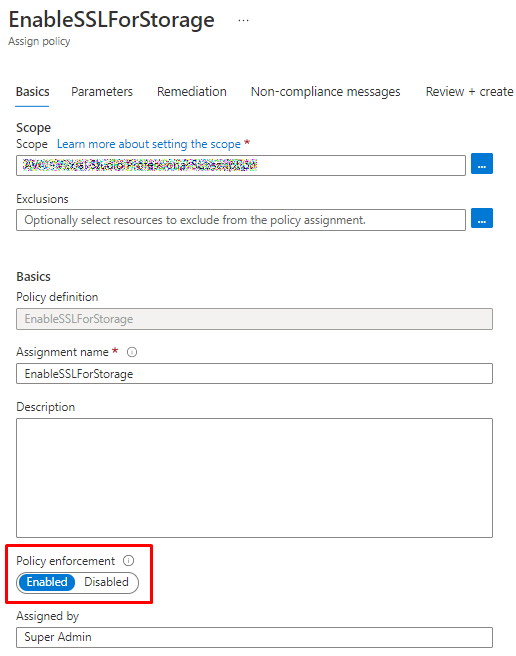
And then the assignment will show like this. From this menu you can enforce the policy
When enforcement mode is disabled, the policy effect isn't enforced (i.e. deny policy won't deny resources). Compliance assessment results are still available.
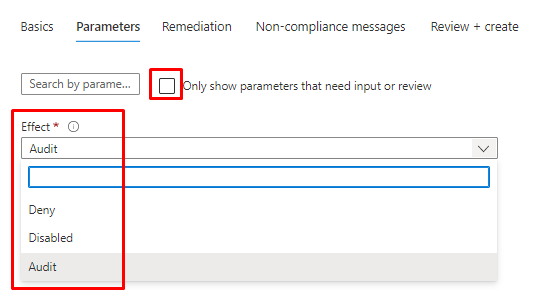
And if You remove the tick from "Only show..." on the next page, you will se effects that have been defined and what the default one.
If you want to do something with the policy, You need Managed identity for it.
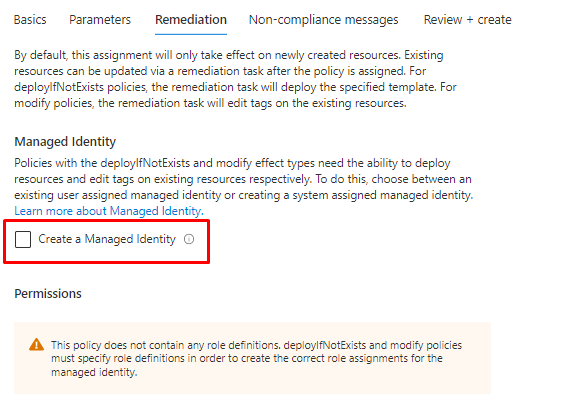
Here instructions how to create a Managed identity and add permissions to it.

Remediate non-compliant resources - Azure Policy
Next you can put a message to display for non-compliance
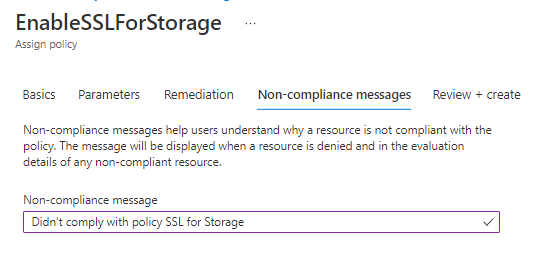
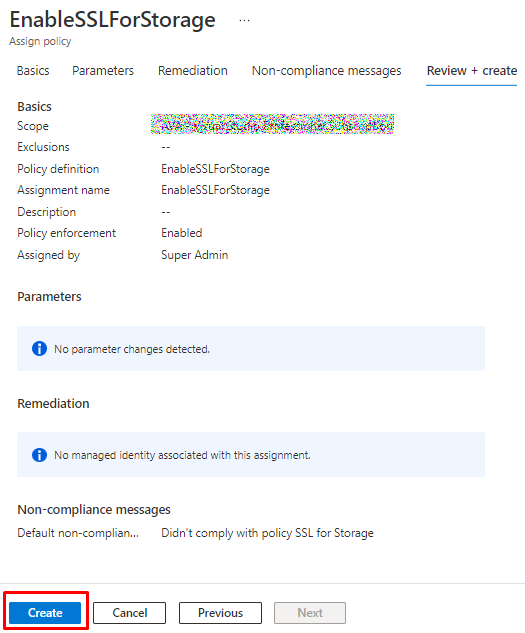
And finally review and create
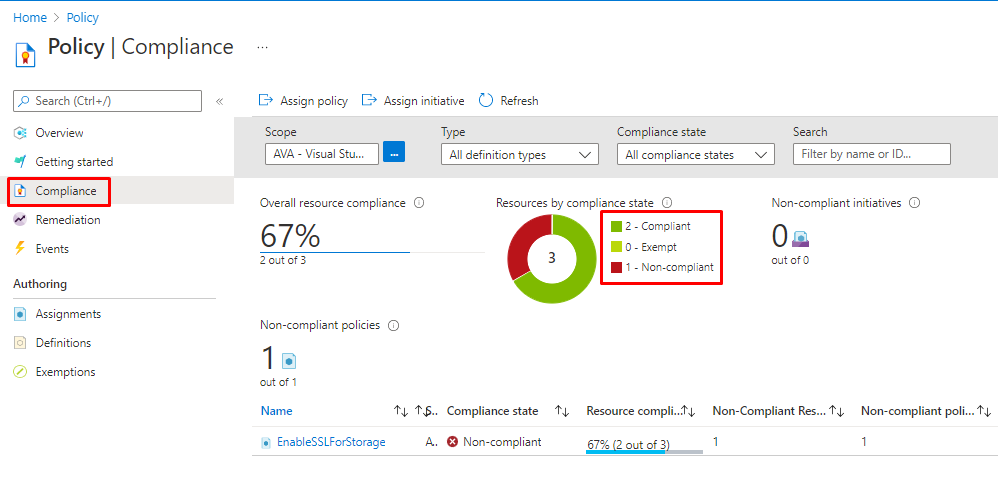
Compliance results
After we have assigned the policy, we can go to compliance and see the results.
For this demo, I created a Storage account with out SSL.
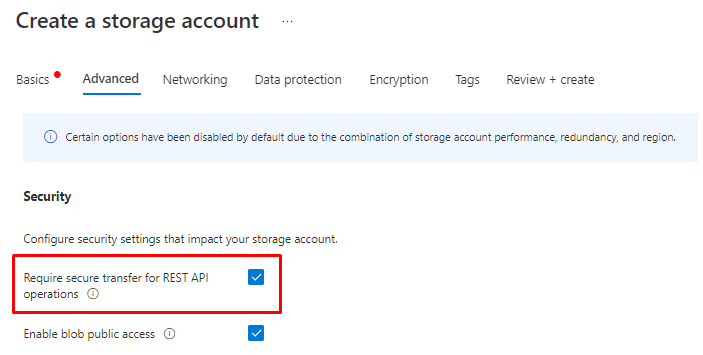
And it will show non-compliant based on the rule we created
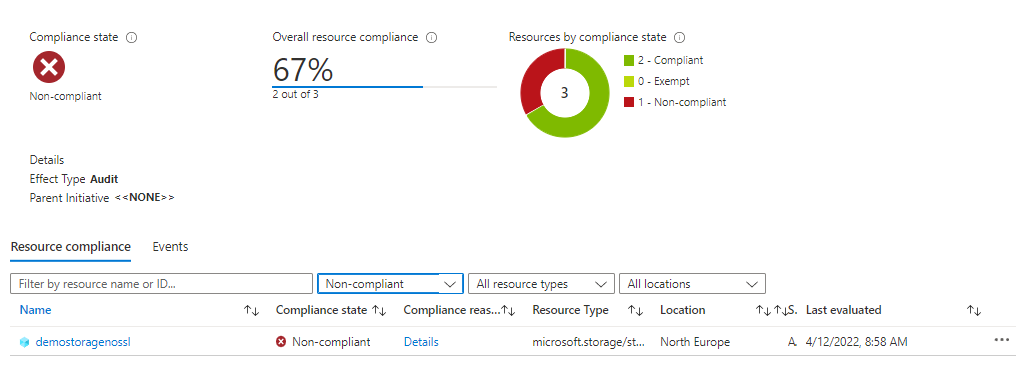
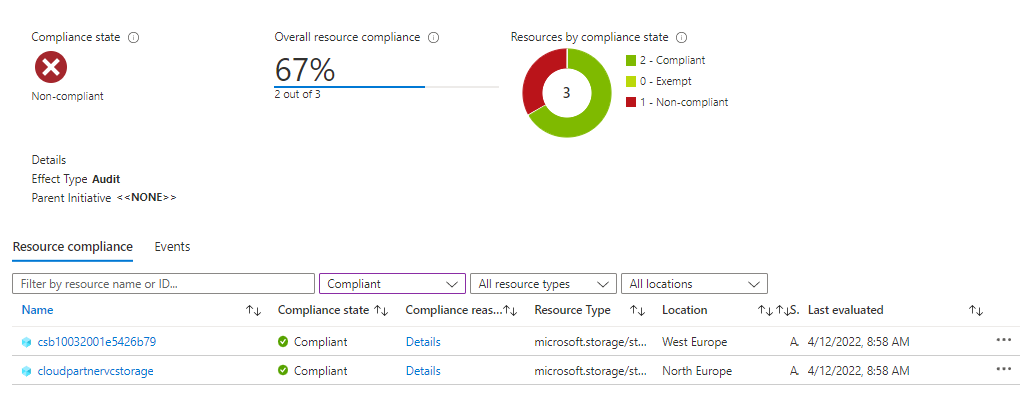
but the other Storage accounts are compliant as they have SSL enabled
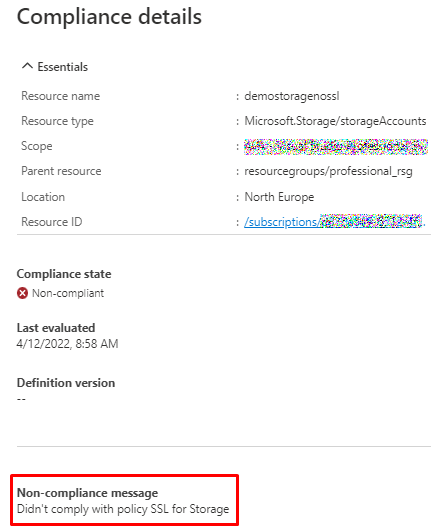
And when we drill down to details, we can see the custom reason we added to the policy
Troubleshooting

Troubleshoot common errors - Azure Policy
Design for data residency requirements
Data residency and DPA
Microsoft has an excellent and throughout PDF for download.

In this document they cover DPA (Microsoft Products and Services Data Protection Addendum) which cover how Microsoft handles your data.
Where my data is located?
Azure AD and it's related components
Microsoft has an excellent Power BI based page for service data residency.
Example for European customers the Azure AD B2B is located in the following
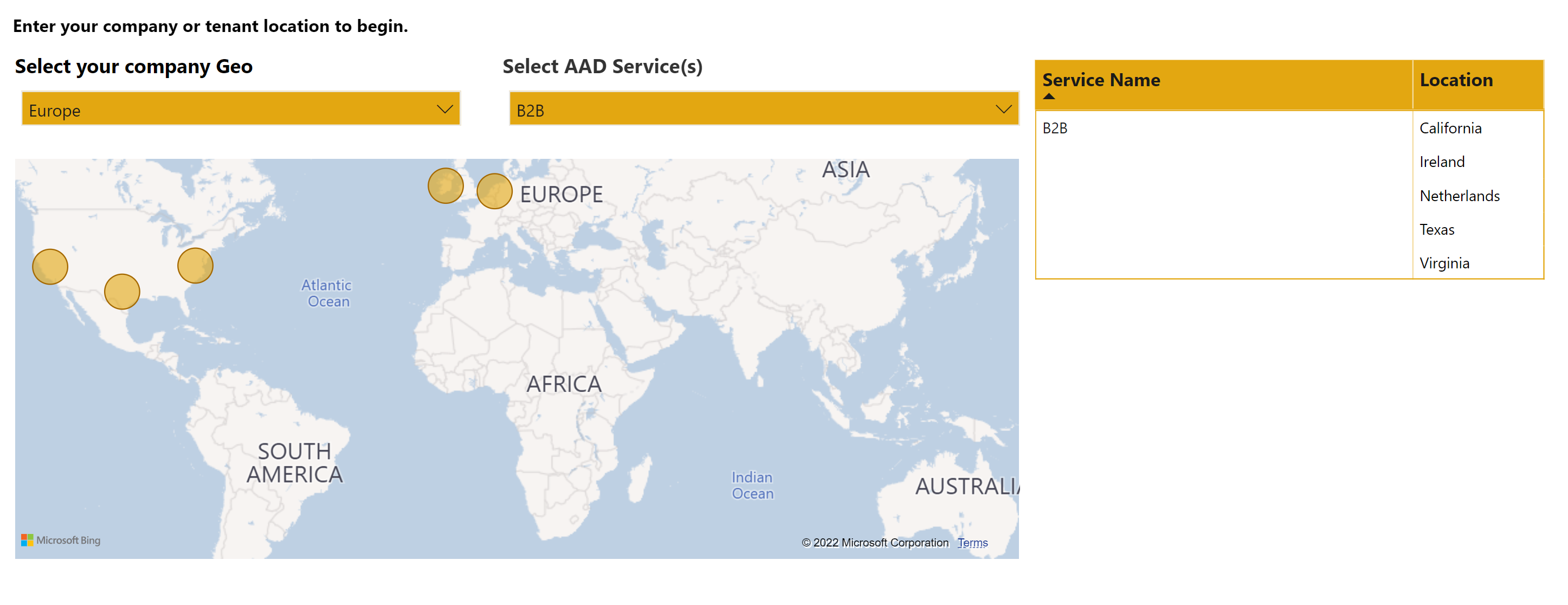
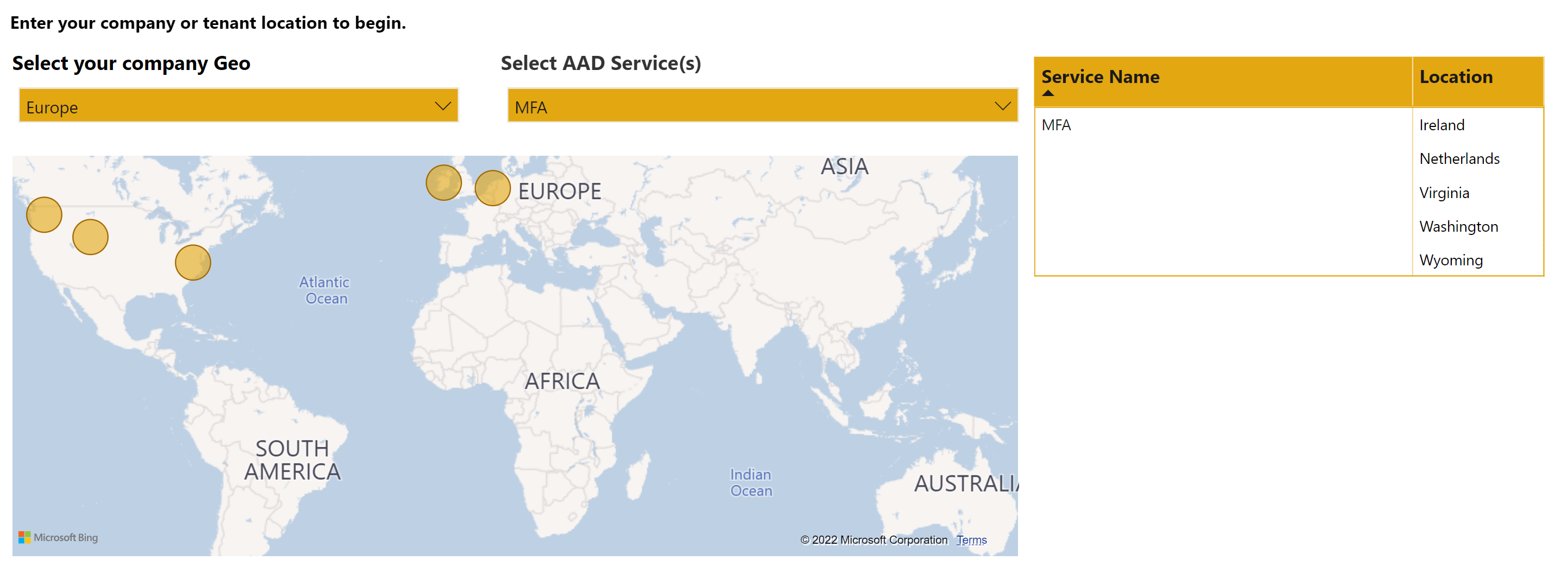
And for MFA in the following
Why you ask?
Azure AD B2B stores invitations with redeem link and redirect URL information in US datacenters. In addition, email address of users that unsubscribe from receiving B2B invitations are also stored in U.S. datacenters.
And for cloud-based Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication, authentication is complete in the closest datacenter to the user. Datacenters for Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication exist in North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific.
- Multi-factor authentication using phone calls originate from datacenters in the customer's region and are routed by global providers.
- Multi-factor authentication using SMS is routed by global providers.
- Multi-factor authentication requests using the Microsoft Authenticator app push notifications that originate from EU datacenters are processed in EU datacenters.
- Device vendor-specific services, such as Apple Push Notifications, may be outside Europe.
- Multi-factor authentication requests using OATH codes that originate from EU datacenters are validated in the EU.
For EU customers

Identity data storage for European customers - Azure AD - Microsoft Entra
And for my Finnish customers
For Finnish customers the deal will be different in the future. Microsoft will build a data center region to Finland.

Microsoft announces intent to build a new datacenter region in Finland, accelerating sustainable digital transformation and enabling large scale carbon-free district heating - Microsoft News Centre Europe
Microsoft 365

Microsoft 365 data locations - Microsoft 365 Enterprise
Moving data to new region
Microsoft provides a data residency option to eligible Microsoft 365 customers who are covered by the datacenter geos listed in the table above. With this option, eligible customers with data residency requirements can request migration of their organization's core customer data at rest to their new datacenter geo. Microsoft will offer a committed deadline to all eligible customers who request migration during the enrollment window. Review the How to request your data move page for more details about the open enrollment window for your datacenter geo and the steps to enroll into the program. Data moves can take up to 24 months after the request period ends to complete.
We introduce no unique capabilities, features or compliance certifications with the new datacenter geo.
The complexity, precision and scale at which we need to perform data moves within a globally operated and automated environment prohibit us from sharing when a data move is expected to complete for your tenant or any other single tenant. Customers will receive one confirmation in Message Center per participating service when its data move has completed.
Data moves are a back-end service operation with minimal impact to end-users. Features that can be impacted are listed on the During and after your data move page. We adhere to the Microsoft Online Services Service Level Agreement (SLA) for availability so there is nothing that customers need to prepare for or to monitor during the move. Notification of any service maintenance is done if needed.
Data moves to the new datacenter geo are completed at no additional cost to the customer.
Process

How to request your data move - Microsoft 365 Enterprise
Translate privacy requirements into requirements for security solutions
Cloud governance
Cloud governance is an iterative process. For organizations with existing policies that govern on-premises IT environments, cloud governance should complement those policies. The level of corporate policy integration between on-premises and the cloud varies depending on cloud governance maturity and the nature of the digital estate in the cloud. As the cloud estate changes over time, so do cloud governance processes and policies. Use the following exercises to help you start building your initial governance foundation:
- Establish your methodology: Establish a basic understanding of the methodology that drives cloud governance in the Cloud Adoption Framework to begin thinking through the end state solution.
- Use the governance benchmark tool: Assess your current state and future state to establish a vision for applying the framework.
- Establish an initial governance foundation: Begin your governance journey with a small, easily implemented set of governance tools. This initial governance foundation is called a minimum viable product (MVP).
- Improve your initial governance foundation: Throughout implementation of the cloud adoption plan, iteratively add governance controls to address tangible risks as you progress toward the end state.
GDPR
GDPR regulates peoples own information. Basically it's saying that you have the right to know where your information is used and you can ask to be forgotten.

General Data Protection Regulation - Microsoft GDPR
Audit reports
Microsoft has a trust portal with all the audit reports, you can download them as a registered user.
Service Trust Portal
Research for cloud privacy and security
Excellent study about 10 recommendations for cloud privacy and security
10 recommendations for cloud privacy and security with Ponemon research
Then to the technical properties.
Encryption
First to introduce the different encryption types that you can use and how they differ.
Client-side encryption
Client-side encryption is performed outside of Azure. It includes:
- Data encrypted by an application that’s running in the customer’s datacenter or by a service application.
- Data that is already encrypted when it is received by Azure.
With client-side encryption, cloud service providers don’t have access to the encryption keys and cannot decrypt this data. You maintain complete control of the keys.
Server-side encryption
The three server-side encryption models offer different key management characteristics, which you can choose according to your requirements:
- Service-managed keys: Provides a combination of control and convenience with low overhead.
- Customer-managed keys: Gives you control over the keys, including Bring Your Own Keys (BYOK) support, or allows you to generate new ones.
- Service-managed keys in customer-controlled hardware: Enables you to manage keys in your proprietary repository, outside of Microsoft control. This characteristic is called Host Your Own Key (HYOK). However, configuration is complex, and most Azure services don’t support this model.
Data at rest
The Microsoft cloud employs a wide range of encryption capabilities up to AES-256, giving you the flexibility to choose the solution that’s best for your business.
Data in transit
Microsoft uses and enables the use of industry-standard encrypted transport protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Internet Protocol Security (IPsec).
Encryption keys
All Microsoft-managed encryption keys are properly secured and offer the use of technologies such as Azure Key Vault to help you control access to passwords, encryption keys, and other secrets.
Different encryption stores (Microsoft solutions)
Azure Managed HSM
Azure Key Vault Managed HSM (Hardware Security Module) is a fully managed, highly available, single-tenant, standards-compliant cloud service that enables you to safeguard cryptographic keys for your cloud applications, using FIPS 140-2 Level 3 validated HSMs.

Azure Managed HSM Overview - Azure Managed HSM
Key vault
Azure Key Vault has two service tiers: Standard, which encrypts with a software key, and a Premium tier, which includes hardware security module(HSM)-protected keys.

Azure Key Vault Overview - Azure Key Vault
Supported services per key type and size
All Microsoft services are encrypted by default with Server-Side and using Service-Managed keys. You change this if needed.
The Azure services that support each encryption model:
Note! The RSA key length is the one mentioned in the documentation, not more, not less.
| Product, Feature, or Service | Server-Side Using Service-Managed Key | Server-Side Using Customer-Managed Key | Client-Side Using Client-Managed Key |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI and Machine Learning | |||
| Azure Cognitive Search | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Cognitive Services | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Machine Learning | Yes | Yes | - |
| Content Moderator | Yes | Yes | - |
| Face | Yes | Yes | - |
| Language Understanding | Yes | Yes | - |
| Personalizer | Yes | Yes | - |
| QnA Maker | Yes | Yes | - |
| Speech Services | Yes | Yes | - |
| Translator Text | Yes | Yes | - |
| Power BI | Yes | Yes, RSA 4096-bit | - |
| Analytics | |||
| Azure Stream Analytics | Yes | Yes**, including Managed HSM | - |
| Event Hubs | Yes | Yes | - |
| Functions | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Analysis Services | Yes | - | - |
| Azure Data Catalog | Yes | - | - |
| Azure HDInsight | Yes | All | - |
| Azure Monitor Application Insights | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Monitor Log Analytics | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Data Explorer | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Data Factory | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| Azure Data Lake Store | Yes | Yes, RSA 2048-bit | - |
| Containers | |||
| Azure Kubernetes Service | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| Container Instances | Yes | Yes | - |
| Container Registry | Yes | Yes | - |
| Compute | |||
| Virtual Machines | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| Virtual Machine Scale Set | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| SAP HANA | Yes | Yes | - |
| App Service | Yes | Yes**, including Managed HSM | - |
| Automation | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Functions | Yes | Yes**, including Managed HSM | - |
| Azure portal | Yes | Yes**, including Managed HSM | - |
| Logic Apps | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure-managed applications | Yes | Yes**, including Managed HSM | - |
| Service Bus | Yes | Yes | - |
| Site Recovery | Yes | Yes | - |
| Databases | |||
| SQL Server on Virtual Machines | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Azure SQL Database | Yes | Yes, RSA 3072-bit, including Managed HSM | Yes |
| Azure SQL Managed Instance | Yes | Yes, RSA 3072-bit, including Managed HSM | Yes |
| Azure SQL Database for MariaDB | Yes | - | - |
| Azure SQL Database for MySQL | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure SQL Database for PostgreSQL | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Synapse Analytics | Yes | Yes, RSA 3072-bit, including Managed HSM | - |
| SQL Server Stretch Database | Yes | Yes, RSA 3072-bit | Yes |
| Table Storage | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Azure Cosmos DB | Yes (learn more) | Yes (learn more) | - |
| Azure Databricks | Yes | Yes | - |
| Azure Database Migration Service | Yes | N/A* | - |
| Identity | |||
| Azure Active Directory | Yes | - | - |
| Azure Active Directory Domain Services | Yes | Yes | - |
| Integration | |||
| Service Bus | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Event Grid | Yes | - | - |
| API Management | Yes | - | - |
| IoT Services | |||
| IoT Hub | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| IoT Hub Device Provisioning | Yes | Yes | - |
| Management and Governance | |||
| Azure Managed Grafana | Yes | - | N/A |
| Azure Site Recovery | Yes | - | - |
| Azure Migrate | Yes | Yes | - |
| Media | |||
| Media Services | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Security | |||
| Microsoft Defender for IoT | Yes | Yes | - |
| Microsoft Sentinel | Yes | Yes | - |
| Storage | |||
| Blob Storage | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | Yes |
| Premium Blob Storage | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | Yes |
| Disk Storage | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| Ultra Disk Storage | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| Managed Disk Storage | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| File Storage | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| File Premium Storage | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| File Sync | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | - |
| Queue Storage | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | Yes |
| Data Lake Storage Gen2 | Yes | Yes, including Managed HSM | Yes |
| Avere vFXT | Yes | - | - |
| Azure Cache for Redis | Yes | N/A* | - |
| Azure NetApp Files | Yes | Yes | - |
| Archive Storage | Yes | Yes | - |
| StorSimple | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Azure Backup | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Data Box | Yes | - | Yes |
| Data Box Edge | Yes | Yes | - |
* This service doesn't persist data. Transient caches, if any, are encrypted with a Microsoft key.
** This service supports storing data in your own Key Vault, Storage Account, or other data persisting service that already supports Server-Side Encryption with Customer-Managed Key.
If you want to read more on Key Vault, read my posts below
Section 15 - Secure data and applications - Configure and manage Azure Key Vault
Key auto-rotation in Azure Key Vault now GA!
Serverless security
Microsoft has an excellent PDF also for Serverless security designs.
Things to remember
Microsoft different models and portal for making your environment compliant:
- CAF (Cloud Adoption Framework
- Well-Architected Framework
- Azure Architecture Center
- Security best practices
- Workload prioritizing
- Microsoft Learn
Available regulatory standards:
- PCI-DSS v3.2.1:2018
- SOC TSP
- NIST SP 800-53 R4
- NIST SP 800 171 R2
- UK OFFICIAL and UK NHS
- Canada Federal PBMM
- Azure CIS 1.1.0
- HIPAA/HITRUST
- SWIFT CSP CSCF v2020
- ISO 27001:2013
- New Zealand ISM Restricted
- CMMC Level 3
- Azure CIS 1.3.0
- NIST SP 800-53 R5
- FedRAMP H
- FedRAMP M
How to use Defender for Cloud and Azure Policy to meet your regulation standards.
On M365 side the same for Purview Compliance Manager
How Secure score is defined in M365
| Type | Assigned score |
|---|---|
| Preventative mandatory | 27 |
| Preventative discretionary | 9 |
| Detective mandatory | 3 |
| Detective discretionary | 1 |
| Corrective mandatory | 3 |
| Corrective discretionary | 1 |
In example for MFA in Defender for Cloud
| Secure score | Security control and description | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | Enable MFA – Defender for Cloud places a high value on multi-factor authentication (MFA). Use these recommendations to secure the users of your subscriptions. There are three ways to enable MFA and be compliant with the recommendations: security defaults, per-user assignment, conditional access policy. Learn more about these options in Manage MFA enforcement on your subscriptions. | – MFA should be enabled on accounts with owner permissions on subscriptions – MFA should be enabled on accounts with write permissions on subscriptions |
Data residency and where the data is located and how to move it if needed.
What services are global and what can be moved.
Different key storing services and encryption models and what are the limitations.